The human brain has yet to explain the origin of one its defining features — the deep fissures and convolutions that increase its surface area and allow for rational and abstract thoughts.
An international collaboration of scientists from the Yale School of Medicine and Turkey may have discovered humanity’s beneficiary — a tiny variation within a single gene that determines the formation of brain convolutions — they reported online May 15 in the journal Nature Genetics.
A genetic analysis of a Turkish patient whose brain lacks the characteristic convolutions in part of his cerebral cortex revealed that the deformity was caused by the deletion of two genetic letters from 3 billion in the human genetic alphabet. Similar variations of the same gene, called laminin gamma3 (LAMC3), were discovered in two other patients with similar abnormalities.
“The demonstration of the fundamental role of this gene in human brain development affords us a step closer to solve the mystery of the crown jewel of creation, the cerebral cortex,” said Murat Gunel, senior author of the paper and the Nixdorff-German Professor of Neurosurgery, co-director of the Neurogenetics Program and professor of genetics and neurobiology at Yale.
The folding of the brain is seen only in mammals with larger brains, such as dolphins and apes, and is most pronounced in humans. These fissures expand the surface area of the cerebral cortex and allow for complex thought and reasoning without taking up more space in the skull. Such foldings aren’t seen in mammals such as rodents or other animals. Despite the importance of these foldings, no one has been able to explain how the brain manages to create them. The LAMC3 gene — involved in cell adhesion that plays a key role in embryonic development — may be crucial to the process.
An analysis of the gene shows that it is expressed during the embryonic period that is vital to the formation of dendrites, which form synapses or connections between brain cells. “Although the same gene is present in lower organisms with smooth brains such as mice, somehow over time, it has evolved to gain novel functions that are fundamental for human occipital cortex formation and its mutation leads to the loss of surface convolutions, a hallmark of the human brain,” Gunel said.
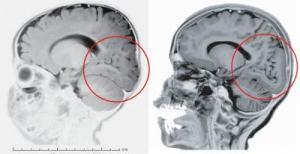
Image caption: On the left, the occipital region of a normal human brain is circled. On the right, the same area of the brain of a subject with mutation of LAMC3 gene is smooth, and lacks normal folds and convolutions. (Credit: courtesy of Yale University)
z12efjhalyjgtda5g04cjf2y3kaexffrgek
 Kingsley Idehen
112399767740508618350
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Google+
Kingsley Idehen
112399767740508618350
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Google+
 Kingsley Idehen
112399767740508618350
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Google+
Kingsley Idehen
112399767740508618350
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Google+
Reshared post from Derya Unutmaz
The human brain has yet to explain the origin of one its defi...
tEslBdyia3F-fSgIabIB5V5hd0vEbfg3nJ_ndBMtQpTS0tpZGqOnp13lzy4C0b7NzcwZ0MCtwcg
 Stan Weddle
111861249122958136216
Are we lucky or what?
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Stan Weddle
111861249122958136216
Are we lucky or what?
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
 Stan Weddle
111861249122958136216
Are we lucky or what?
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Stan Weddle
111861249122958136216
Are we lucky or what?
Aug 25, 2011
Aug 25, 2011
Permalink
tEslBdyia3F-fSgIabIB5V5hd0vEbfg3nJ_ndBMtQpTS0tpZGqOnp5e0rBzetmHLDa7TJ64uKJg
 Lise Bjerregaard Nielsen
104873021163951124714
"A genetic analysis of a Turkish patient whose brain lacks the characteristic convolutions in part of his cerebral cortex revealed that the deformity was caused by the deletion of two genetic letters from..."
Lise Bjerregaard Nielsen
104873021163951124714
"A genetic analysis of a Turkish patient whose brain lacks the characteristic convolutions in part of his cerebral cortex revealed that the deformity was caused by the deletion of two genetic letters from..."
Am I the only one who's wondering how this Turkish patient presented?
I mean, this person must have had some pretty severe symptoms - but which, and exactly how severe?
Not that the rest of the text is not very interesting reading, it certainly is.
I'd just really like to have that extra dimension. Aug 25, 2011 Aug 25, 2011
 Lise Bjerregaard Nielsen
104873021163951124714
"A genetic analysis of a Turkish patient whose brain lacks the characteristic convolutions in part of his cerebral cortex revealed that the deformity was caused by the deletion of two genetic letters from..."
Lise Bjerregaard Nielsen
104873021163951124714
"A genetic analysis of a Turkish patient whose brain lacks the characteristic convolutions in part of his cerebral cortex revealed that the deformity was caused by the deletion of two genetic letters from..."Am I the only one who's wondering how this Turkish patient presented?
I mean, this person must have had some pretty severe symptoms - but which, and exactly how severe?
Not that the rest of the text is not very interesting reading, it certainly is.
I'd just really like to have that extra dimension. Aug 25, 2011 Aug 25, 2011
tEslBdyia3F-fSgIabIB5V5hd0vEbfg3nJ_ndBMtQpTS0tpZGqOnp0rJCI4qivaWw4cunB7P3U0
 Carsten Ullrich
108246341890892380303
Looking forward to some cool horror flicks about creatures that escape from lab when some mad scientist manipulates this gene in reptiles and insects.
Aug 26, 2011
Aug 26, 2011
Carsten Ullrich
108246341890892380303
Looking forward to some cool horror flicks about creatures that escape from lab when some mad scientist manipulates this gene in reptiles and insects.
Aug 26, 2011
Aug 26, 2011
 Carsten Ullrich
108246341890892380303
Looking forward to some cool horror flicks about creatures that escape from lab when some mad scientist manipulates this gene in reptiles and insects.
Aug 26, 2011
Aug 26, 2011
Carsten Ullrich
108246341890892380303
Looking forward to some cool horror flicks about creatures that escape from lab when some mad scientist manipulates this gene in reptiles and insects.
Aug 26, 2011
Aug 26, 2011