| Not logged in : Login |
About: What Is the Receivables Turnover Ratio? How Amazon Receivables Management Helps Its Explosive Growth Goto Sponge NotDistinct Permalink

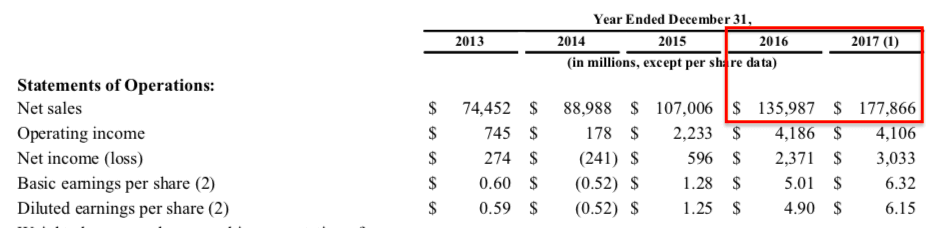
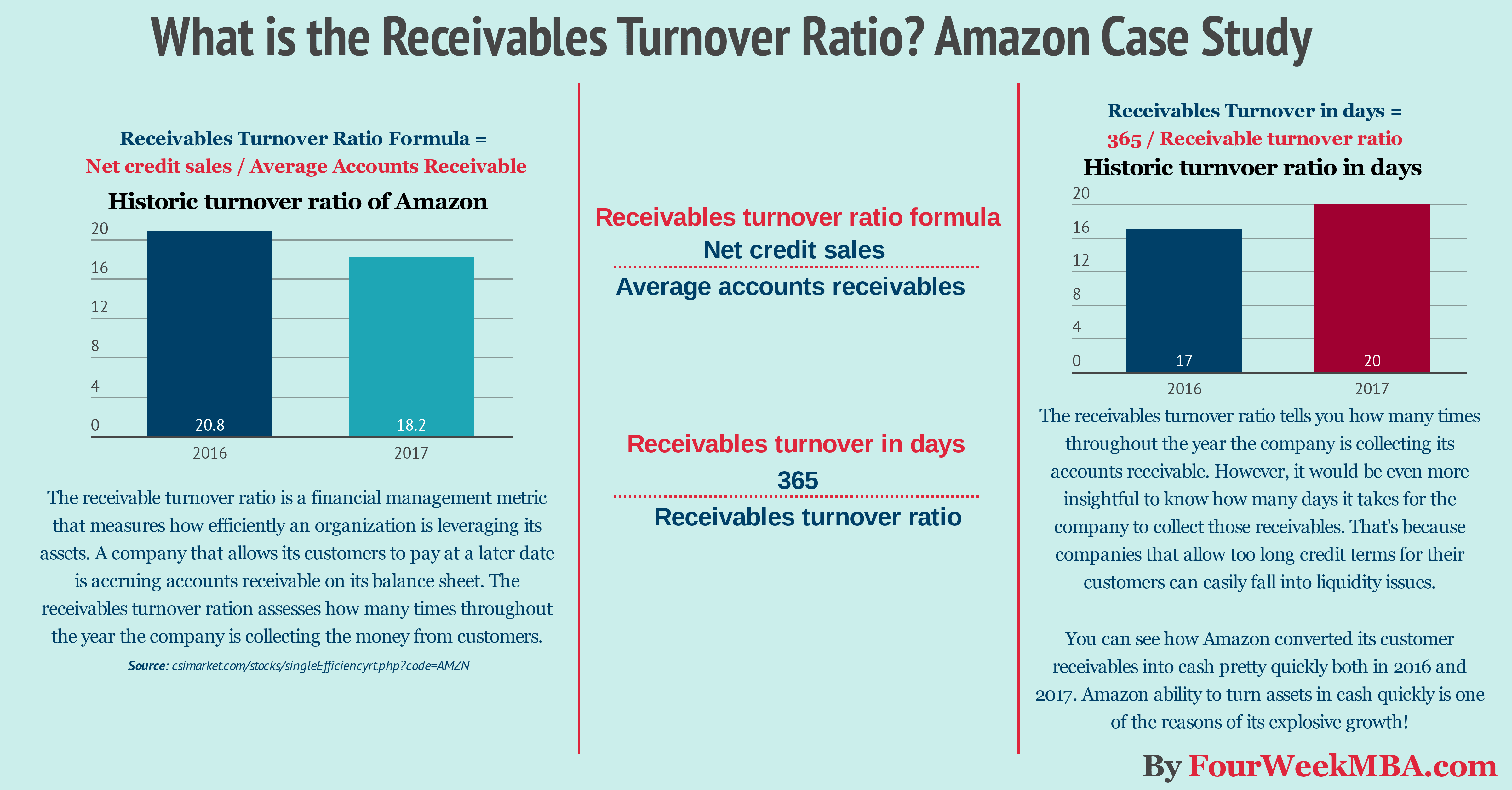
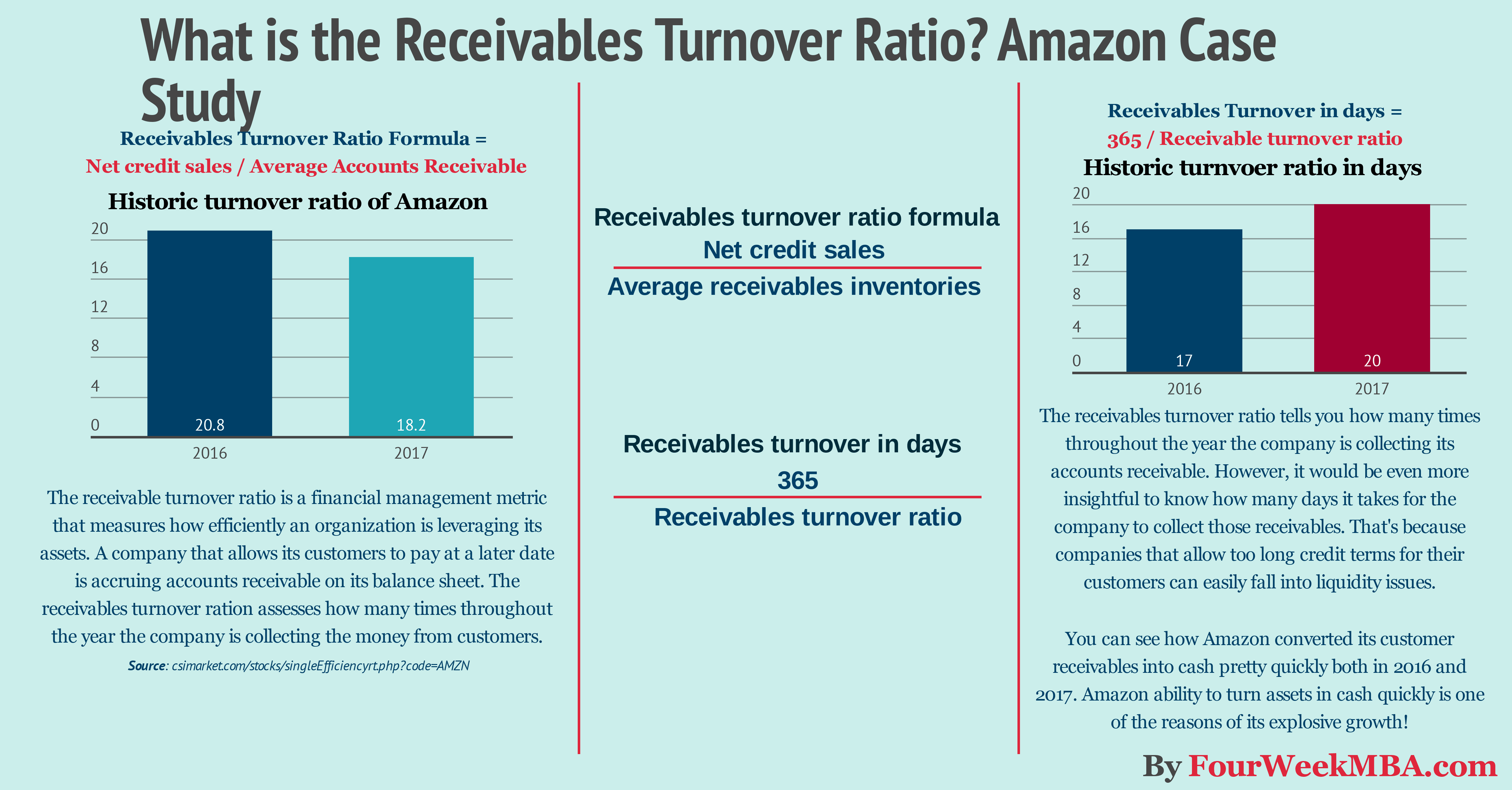
The receivable turnover ratio is a financial management metric that measures how efficiently an organization is leveraging its assets. A company that allows its customers to pay at a later date is accruing accounts receivable on its balance sheet. The receivables turnover ration assesses how many times throughout the year the company is collecting the money from customers. What is account receivables? They include the amount of money to be received by customers. According to the matching principle, revenue is reported as soon as realizable. Therefore, the customer did not pay yet for the service already rendered, the money owed will be shown under Accounts Receivable, with the heading of Current Assets. The AR can be one of the most challenging accounts on the BS when it comes to quantifying it. Indeed, at times is very complicated to determine the amount of receivable that can be collected. Example: Imagine you sell raw materials to companies that produce peanut butter. Your customers are companies who have large operations, and for such reasons, they pay within 90 days from receiving the raw materials. One of your main customers owes you $100K. Its business though is in distress and in few months may be bankrupt. How would you know which percentage of the $100K can be collected? Truth is you won’t know until the company will be liquidated and assets sold. Imagine you can collect 30% of the outstanding $100K. Overall you recovered $30K. What about the remaining $70K? Well, this will become a bad debt. Therefore, you will decrease the AR by 70K and expense this amount as Bad Debt. In conclusion, you understand that AR can be tricky. In a few cases, the number you see on the BS can be misleading. The receivables turnover ratio explained The main aim of the receivables turnover ratio is to understand whether a company is efficiently collecting money from its customers. In fact, in many cases when purchasing a product or service companies allow customers to pay in 30 to 90 days (generally). That means in the meanwhile the company will have on its balance sheet an accounts receivable item. That implies the company is not getting cash from the transaction. Cash is critical for the short-term success of any organization. For instance, take the case of a company that has a high turnover but no cash in the bank. That would lead to a liquidity crisis that in many cases leads to bankruptcy. Thus, keeping an eye to the receivables turnover ratio can be similar to measuring your body temperature. When you start to be short of cash, the first place you might want to look into is the accounts receivable, to make sure you don't have uncollected money from your customers. How do you measure it? Receivables Turnover Ratio Formula = Net credit sales / Average Accounts Receivable The net credit sales are merely the net sales depured of sales returns and sales allowances. Take for instance the case in which a company has a net credit sales of $1 million and accounts receivables for 95 thousand dollars; the receivables turnover ratio would be 10.52. Net credit sales / Average Accounts Receivable $1 million / $95 thousand = 10.52 What does that mean? It means that over the year (if computed on a yearly basis) the company collected it accounts receivables 10.52 times. The higher the number, the more the company is working with a high level of cash as it is quickly turning its assets in cash for the business. If we take a small additional step, we can gain another critical insight. Receivables turnover in days The receivables turnover ratio tells you how many times throughout the year the company is collecting its accounts receivable. However, it would be even more insightful to know how many days it takes for the company to collect those receivables. That's because companies that allow too long credit terms for their customers can quickly fall into liquidity issues. What credit terms should a company have? In general no longer than 90 days. Of course the shorter, the better. How do you assess the receivables turnover in days? Take 365 (number of days in a year ) and divide it by the receivables turnover ratio. Receivables Turnover in Days Ratio Formula = Receivables turnover ratio / 365 � In the example above the receivable turnover ratio was 10.52. Thus, we divide 365 by 10.52, and we get 34. In other words, it takes 34 days to convert the accounts receivables in cash for the business! 365 / 10.52 = 34 days to convert accounts receivable in cash for the business Let's dive now into a practical case study. Let's see how Amazon manages its accounts receivables! How Amazon is running on low accounts receivables I decided to cover Amazon as that is one of the most interesting case studies out there. In fact, as explained in the article about Amazon cash conversion cycle thanks also in part on how the company manages its accounts receivables, Amazon is a cash machine! In other words, the company operates at a very tight net income margin yet it generates a lot of cash thanks also to its low accounts receivable which Amazon invests in the business for future growth. That is clear if we look at its balance sheet: For the sake, if this analysis let's take Amazon revenues for the last two years: We can average the net sales for the last two years ((135,987 + 177,866) / 2) and divide it by the average accounts receivable for the last two years ((8,339 + 13,164) / 2); we get a 19.31 receivables turnover ratio. I could have adjusted it to reflect sales allowances, but the number change would be minimal, thus not necessary for the sake of our analysis on the business strategy. If we take 365 and divide it by 19.31, we get 18.9 days! In short, Amazon converts its receivables in cash pretty quickly. Is this good or bad? It's good. However, financial ratios can tell us something only when we compare them to previous years performance and to the industry it belongs to. Source: reuters.com Everyone knows that "cash is king" for business success. Amazon made this statement its mantra. As you can see compared to the sector Amazon receivable turnover if way lower. As specified on its 2017 annual report: Because of our model we are able to turn our inventory quickly and have a cash-generating operating cycle. On average, our high inventory velocity means we generally collect from consumers before our payments to suppliers come due. We've already seen this phenomenon in the cash conversion cycle of Amazon, which regarding business strategy is the most incredible fit the company has achieved. Why? Amazon gets the cash from its customers and uses it to finance its growth, which has become explosive. That is how Amazon can take over one industry over the other! Amazon receivables turnover ration and receivables turnover ration in days Handpicked related content: How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell Amazon Case Study: Why from Product to Subscription You Need to “Swallow the Fish” What Is Cash Conversion Cycle? Amazon Cash Machine Business Model Explained What Is the Inventory Turnover Ratio? How Inventory Efficiency Can Fuel Business Growth Resources for your business: What Is a Business Model? 30 Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
| Attributes | Values |
|---|---|
| type | |
| label |
|
| label |
|
| Description |
|
| depiction | |
| name |
|
| url |
Alternative Linked Data Documents: PivotViewer | iSPARQL | ODE Content Formats:
![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png) RDF
RDF
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png) ODATA
ODATA
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[odata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png) Microdata
Microdata
![[microdata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png) About
About


![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)
OpenLink Virtuoso version 08.03.3330 as of Mar 11 2024, on Linux (x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25), Single-Server Edition (7 GB total memory, 6 GB memory in use)
Data on this page belongs to its respective rights holders.
Virtuoso Faceted Browser Copyright © 2009-2024 OpenLink Software