| Not logged in : Login |
About: How Does Groupon Make Money? Groupon Business Model In A Nutshell Goto Sponge NotDistinct Permalink

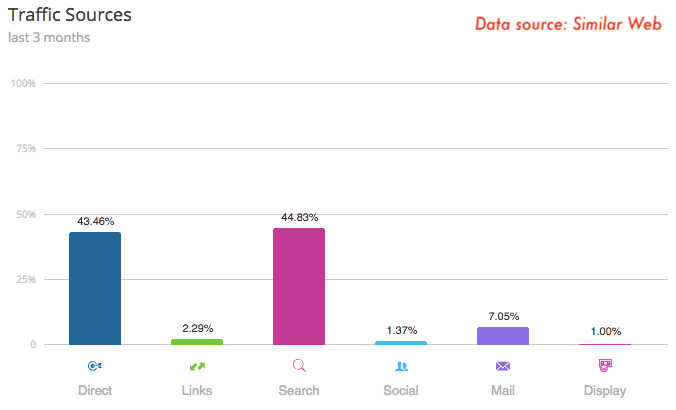
Groupon business model is a two-sided marketplace where local consumers meet deals from local merchants. The company makes money by selling local and travel services and goods. Its value proposition based on attracting local customers to local merchants is quite compelling. Local consumers instead get savings and discounts that they would not get elsewhere. The company measures its financial success in gross billings and revenues growth. Groupon generated over $2.8 billion in 2017, by selling its goods and services directly via its websites and mobile app, and indirectly via third-party affiliate sites, who get a commission for each sale. Related: How Does Airbnb Make Money? Airbnb Peer To Peer Business Model In A Nutshell Groupon business snapshot Groupon business model is based on a local e-commerce marketplace that connects merchants to consumers by offering goods and services at a discount. Groupon in part replaces the traditional media that local businesses have used over the years to generate sales at a local level. This includes: yellow pages direct mail newspaper radio television and online advertisements The value proposition is quite simple: Groupon attracts customers to merchants, which otherwise would have missed. Consumers get savings and discounts that they would usually not get elsewhere. Related: What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained Those offers are primarily run on groupon.com sites in many countries, and mobile applications. The offerings are organized into three primary categories: Local (service): revenues are primarily generated through Groupon relationships with local and national merchants Goods (product): direct revenues from transactions in which Groupon sell merchandise inventory directly to customers, and third-party revenues and Travel (service): Groupon features travel offers at both discounted and market rates Distribution strategy and marketing mix: a two-sided marketplace needs both marketing and sales capabilities When deciding whether allocate marketing vs. sales resources, it is critical to understand the value of a lead and potential customer on the one hand. Thus, if a company sells expensive products made for a specific and limited target business development and sales are the key ingredient for its success. Yet if the company sells a low-priced product which is well-suited for a mass market or consumers, then marketing will be the best option available. On the other hand, when it comes to the acquisition and distribution process of a two-sided marketplace, it is essential to consider the acquisition process from two perspectives. For instance, the two principal partners Groupon has to create value for are: local merchants willing to offer discounts in exchange for qualified local customers and local consumers ready to buy from local merchants This also implies a two-sided distribution strategy, where each of those key players will be drawn to the platform with either sales or marketing. The value of a merchant brought to Groupon is intrinsically higher than the value of a local consumer. Therefore, Groupon will use sales processes and support to nurture the relationships with those local merchants. Instead, to acquire local consumers, Groupon uses a marketing mix made of several marketing activities to keep the platform appealing for its local consumers which can find the offer they need. The two ways of access to the platform are: the website groupon.com and the mobile app Let's now look in detail at Groupon marketing and sales activities to draw local consumers and local merchants to the platform. Marketing as the primary driver of acquisition of local consumers Groupon uses a variety of marketing channels with a direct to customers business model by making its deal offerings available through its marketplaces. The primary driver for consumers access is the Groupon mobile application. Indeed, in the fourth quarter of 2017, over 69% of Groupon global transactions happened on mobile devices. This makes marketing a critical ingredient of Groupon growth strategy and an essential component of its distribution strategy. To have some context in 2017 Groupon spent 31% of its revenues in marketing (over $400 million). What marketing mix does Groupon use? Search engine optimization For a platform like Groupon that highly depends on visibility from local consumers across the globe, there is no better way to reach them than through search engines. Indeed, search engines present two key advantage: consumers can be targeted based on specific keywords (like, "best SPA deals") consumers can also be targeted based on local keywords (like, "best SPA deals in LA") Therefore, an SEO (search engine optimization) can have a massive ROI for a company and platform like Groupon. Via third-party search engines, consumers across the globe can access to Groupon deals. SEO has the advantage of being organic. In short, consumers get to Groupon based on organic rankings the platform has gained over the years. Search engine marketing Customers can access the Groupon platform also via paid listings on search engines based on bidding keywords. For instance, Google allows through its advertising network to bid on specific keywords that have specific commercial intent. Thus, companies that look for those keywords will probably end up purchasing Groupon deals. This is called search engine marketing or SEM. Email and push notifications. Another key ingredient of Groupon marketing mix is comprised of direct access to consumers via an email list made of subscribers that voluntarily sign up and of push notifications (notification service to send updates on mobile devices). That system allows Groupon a higher control over what offerings to show directly to its consumers and subscribers. Affiliate channels. Another important marketing distribution strategy is based on affiliate marketing. In short, affiliates that send consumers to Groupon offerings via links on their websites get rewarded with a commission. Social and display. The virality of social media is also essential to allow the sharing of dealings from Groupon. Groupon also promotes its offerings using display advertising on websites. Television and other offline. Groupon also started to invest more in offline marketing, such as television advertising, print, and radio. Sales operations as the primary driver of acquisition of local merchants The relationship with the millions of local merchants on Groupon is critical for the long-term success of the business. Those relationships indeed are an essential part of long-term business success. That's also why Groupon, in 2017, had 2,400 merchant sales representatives and sales support staff. They had the role of nurturing merchant relationships and provide local expertise. Beyond merchant sales, Groupon also leverages on deal managers to provide support in areas such as: deal managers editorial merchant services customer service technology merchandising and logistics Deal managers and sales teams work together to optimize deal structure, pricing, discount and geographic mix of deals in respective markets. The editorial department creates written and visual content on the deals offered on the platform. Merchant services representatives help merchants optimize their strategy when deals are offered. And customer service answers customer inquiries in several areas. The technology focuses on the design and development of new features and products, maintenance of the site and mobile platform and improvement of the internal system. While merchandising and logistics are responsible for managing inventory and the flow of products from suppliers to customers. In 2017 Groupon spent over $994 million to support this infrastructure. How does Groupon make money? Source: Groupon 2017 Annual Report Groupon makes money primarily by selling its deals offerings to local consumers based on two primary channels: direct third-party and other Cost of Direct revenues The Company generates direct revenue from merchandise of sale inventory through its Goods category. That is also the reason why the cost of revenues for immediate is way higher than third-party revenues which are recorded on a net basis. Direct revenues also include a cost of inventory, shipping, fulfillment costs, and inventory markdowns. Third-party and other revenue For the third-party merchant, revenue is recorded on a net basis and is presented within third-party revenue. For third-party revenue transactions, cost of revenue includes estimated refunds. The mechanism allows those third-party to earn commissions when customers make purchases using digital coupons via their websites and applications. Key financial metrics Each business financial success is measured according to a set of internal metrics the company uses to assess its growth. At the same time, those metrics are communicated to outside investors to assess the state of advancement of the company. Groupon looks at five key metrics: gross billings revenue gross profit adjusted EBITDA free cash flow A glance at Groupon digital marketing strategy Groupon has a massive reach, with its website alone has over fifty million visits according to Similar Web estimates (this is an estimate and not to be taken as an actual number): Also according to Similar Web Groupon is the first site in the US for Coupons, within the Shopping category. Still, according to Similar Web estimates, the marketing mix is skewed toward two primary channels: direct and organic traffic (via SEO) Those two sources of traffic are critical as on the one hand it points Groupon strong brand and at the same time authoritativeness. Other channels like social, mail and display also play a crucial role. Related business models: A Snapshot Of Booking Business Model How Does Airbnb Make Money? Airbnb Peer To Peer Business Model In A Nutshell Tools and resources for your business: What Is a Business Model? 30 Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business What Is Business Development? The Complete Guide To Business Development Selected business models from the site: How Does Facebook Make Money? Facebook Hidden Revenue Business Model Explained How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell The Trillion Dollar Company: Apple Business Model In A Nutshell How Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model Explained How Does Google Make Money? It’s Not Just Advertising!
| Attributes | Values |
|---|---|
| type | |
| label |
|
| label |
|
| sameAs | |
| Description |
|
| depiction | |
| name |
|
| url | |
| legalName |
|
| http://www.w3.org/2007/ont/link#uri |
Alternative Linked Data Documents: PivotViewer | iSPARQL | ODE Content Formats:
![[cxml]](/fct/images/cxml_doc.png)
![[csv]](/fct/images/csv_doc.png) RDF
RDF
![[text]](/fct/images/ntriples_doc.png)
![[turtle]](/fct/images/n3turtle_doc.png)
![[ld+json]](/fct/images/jsonld_doc.png)
![[rdf+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[rdf+xml]](/fct/images/xml_doc.png) ODATA
ODATA
![[atom+xml]](/fct/images/atom_doc.png)
![[odata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png) Microdata
Microdata
![[microdata+json]](/fct/images/json_doc.png)
![[html]](/fct/images/html_doc.png) About
About


![[RDF Data]](/fct/images/sw-rdf-blue.png)
OpenLink Virtuoso version 08.03.3330 as of Mar 11 2024, on Linux (x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25), Single-Server Edition (7 GB total memory, 5 GB memory in use)
Data on this page belongs to its respective rights holders.
Virtuoso Faceted Browser Copyright © 2009-2024 OpenLink Software